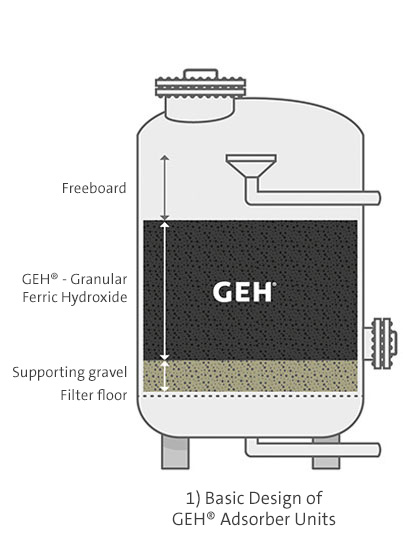
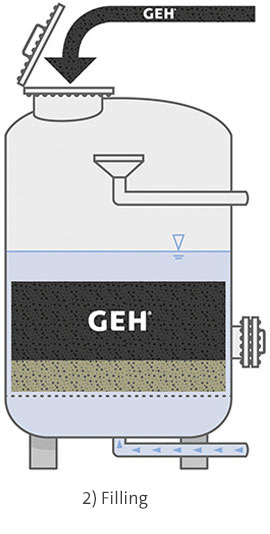
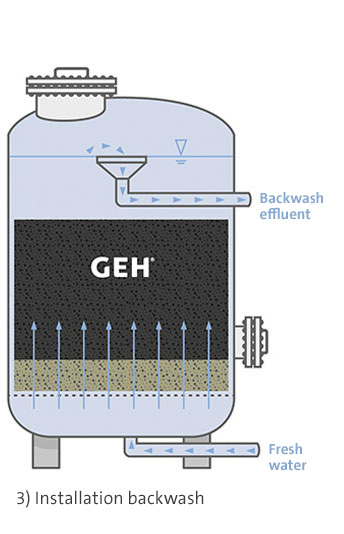
During the adsorption process, arsenic binds to the surface of a solid adsorptive media, or adsorbent. Prior to iron-based adsorbents being developed, activated alumina were primarily used to remove arsenic. Due to the low capacity and hazardous nature of dissolved aluminium, this no longer has any active role to play these days.
Iron-hydroxide adsorbents are the best demonstrated available technology for removing arsenic during drinking water production. Their most significant benefits lie in how simple and safe it is to operate adsorption filters and remove arsenic to a level that is below the detection limit. Moreover, no wastewater streams or contaminated sludges are generated during operation. The removal of arsenic using granular ferric hydroxide occurs selectively – leaving the water’s natural composition unchanged. Both arsenate and arsenite are removed during this process.
Pro
- Simple plant configuration and uncomplicated operation
- Very high capacity due to high arsenic selectivity
- High plant availability and low maintenance requirements
- Established technology used globally in over 2000 locations
- Easy removal without sludge treatment
Contra
$- Residence time depends on water matrix
- Adsorbent needs to be replaced at regular intervals